Featured Work
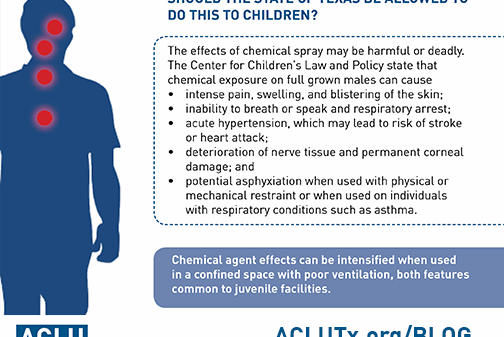
Should the State of Texas Be Allowed to Do This to Children?
A report to the Council of Juvenile Correctional Administrators found that facilities with high numbers of restraint and chemical incidents are more likely to produce higher rates of safety problems because of youth and staff injury, suicidal behavior, and fear among the youths from injury by staff.
The reported higher rate of incidents explain why the Council of Juvenile Correctional Administrators’ annual, national survey revealed only six state juvenile corrections agencies authorizing the use of chemical spray in order to secure the facilities: The low national authorization is due to data that shows negative impacts on the staff, juveniles, and facilities when it is used. The survey also showed that 15 agencies authorized chemical restraints, but not necessarily for the staff to carry on their person. Nine of those 15 agencies only authorize chemical restraint as a last

